ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
Introduction
ELISA is the basic assay technique, known as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (also referred to as EIA: Enzyme Immunoassay) that is carried out to detect and measure antibodies, hormones, peptides and proteins in the blood.
Antibodies are blood proteins produced in response to a specific antigen. It helps to examine the presence of antibodies in the body, in case of certain infectious diseases.
ELISA is a distinguished analysis compared to other antibody-assays as it yields quantitative results and separation of non-specific and specific interactions that take place through serial binding to solid surfaces, which is normally a polystyrene multiwell plate.
Types of ELISA
ELISA tests can be classified into three types depending upon the different methods used for binding between antigen and antibodies, namely:
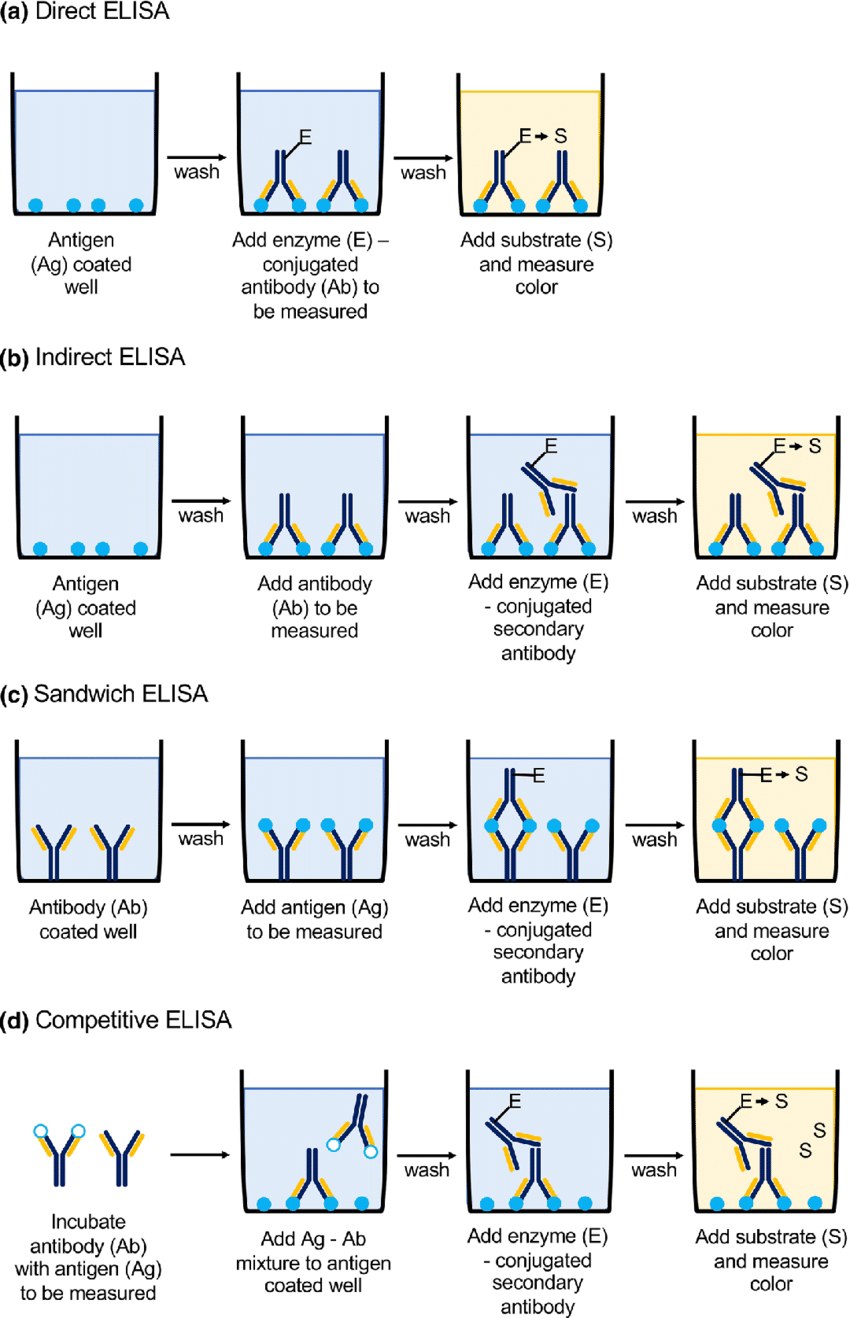
1.Indirect ELISA – Antigen is coated to the microtiter well
2.Sandwich ELISA – Antibody is coated on the microtiter well
3.Competitive ELISA – Microtiter well which is antigen-coated is filled with the antigen-antibody mixture.
1.Indirect ELISA
Indirect ELISA detects the presence of an antibody in a sample.
The antigen is attached to the wells of the microtitre plate.
A sample containing the antibodies is added to the antigen-coated wells for binding with the antigen.
The free primary antibodies are washed away and the antigen-antibody complex is detected by adding a secondary antibody conjugated with an enzyme that can bind with the primary antibody.
All the free secondary antibodies are washed away. A specific substrate is added which gives a coloured product.
The absorbance of the coloured product is measured by spectrophotometry.
2.Sandwich ELISA
Sandwich ELISA helps to detect the presence of antigen in a sample.
The microtitre well is coated by the antibody.
The sample containing the antigen is added to the well and washed to remove free antigens.
Then an enzyme-linked secondary antibody, which binds to another epitope on the antigen is added. The well is washed to remove any free secondary antibodies.
The enzyme-specific substrate is added to the plate to form a coloured product, which can be measured.
3.Competitive ELISA
Competitive ELISA helps to detect antigen concentration in a sample.
The microtitre wells are coated with the antigen.
Antibodies are incubated in a solution having the antigen.
The solution of the antigen-antibody complex is added to the microtitre wells. The well is then washed to remove any unbound antibodies.
More the concentration of antigen in the sample, lesser the free antibodies available to interact with the antigen, which is coated in the well.
The enzyme-linked secondary antibody is added to detect the number of primary antibodies present in the well.
The concentration is then determined by spectrophotometry.
Principle of ELISA
ELISA works on the principle that specific antibodies bind the target antigen and detect the presence and quantity of antigens binding. In order to increase the sensitivity and precision of the assay, the plate must be coated with antibodies with high affinity. ELISA can provide a useful measurement of antigen-antibody concentration.
ELISA Procedure
ELISA is one of the easiest blood tests that can be carried out. It is rapid, quick and requires a blood sample of the patient. The entire procedure of ELISA is mentioned below.
An antibody is attached to a polystyrene plate which is a solid surface and is attracted or has an affinity towards bacteria, other antibodies and hormones.
A microtiter coated with antigen is filled with this antigen-antibody mixture after which free antibodies are removed by washing.
A second antibody specific to primary antibody is added which is usually conjugated with an enzyme.
Free enzyme-linked secondary antibodies are removed by washing the plate.
Finally, the substrate is added. The substrate is converted by the enzyme to form a coloured product, which can be measured by spectrophotometry.
HCG protein which indicates pregnancy is detected by ELISA. A combination of blood or urine sample and purified HCG linked to an enzyme is added to the system. If HCG is absent in the test sample, then only the linked enzyme binds to the solid surface.
The more the substance of interest is present, the more reaction takes place and less of linked enzyme binds to the solid surface. These reactions are indicated usually with a change in the colour of the solution.
Diseases that can be Diagnosed Using ELISA
ELISA can be used to detect some of these conditions:
Ebola
Pernicious anaemia
AIDS
Rotavirus
Lyme disease
Syphilis
Toxoplasmosis
Zika virus
Carcinoma of the epithelial cells
Advantages Of ELISA
Following are some of the advantages of the ELISA technique:
Results fetched from ELISA gives an accurate diagnosis of a particular disease since two antibodies are used.
Can be carried out for complex samples as the antigen is not required to get purified to detect.
It is highly responsive since direct and indirect analysis methods can be carried out.
It is a rapid test, yields results quickly.
Possible detection for ELISA ranges from the quantitative, semi-quantitative, standard curve, qualitative, calibration curve models etc.
Easier to perform and uncomplicated process as compared to other assays which require the presence of radioactive materials.
Applications of ELISA
The applications of ELISA are discussed below:
The presence of antibodies and antigens in a sample can be determined.
It is used in the food industry to detect any food allergens present.
To determine the concentration of serum antibody in a virus test.
During a disease outbreak, to evaluate the spread of the disease, e.g. during recent COVID-19 outbreak, rapid testing kits are being used to determine presence of antibodies in the blood sample.